On a day-to-day basis, it’s difficult to delve into various subjects – even those that interest us most. Research can empower informed decision-making, but the sheer volume of publications can be overwhelming, demanding a significant amount of our precious time. Luckily, we have you covered.
We have selected five pieces of HR-relevant research to facilitate your decision-making process and enhance the effectiveness of organizational practices. Is discrimination in hiring decisions diminishing? How effective is electronic performance management in enhancing worker performance? What strategies can organizations employ to enhance supervisor ratings or to cultivate teams for heightened creativity and innovation? Discover insights into these questions in our summary of this year’s significant research.
Who does hiring discrimination impact most?
Despite growing diversity in the workforce, many individuals continue to encounter discrimination in the labor market. Which specific groups are facing discrimination, and what should recruiters prioritize in addressing these issues? A meta-analysis of hiring discrimination studies from 2005 to 2020 revealed equal severity in discrimination against candidates with disabilities, older individuals, and less physically attractive candidates compared to those with racial or ethnic characteristics. Initially, there was a decline in ethnic-based discrimination in hiring in Western Europe, but no overall reduction was found when considering specific minority groups or at the country level. Notably, discrimination varies among minority groups, with candidates of Arab, Maghrebi, or Middle Eastern origin facing substantial bias, while evidence of discrimination against White European minority applicants is weak. Additionally, the study found higher discrimination against older applicants in Europe compared to the United States. For recruiters, this means that prioritizing measures to reduce discrimination should focus on the most penalized minority groups.
Do male applicants also experience gender discrimination in hiring?
How prevalent is gender discrimination in hiring, and have societies made meaningful strides toward equality of opportunity? To address this, researchers conducted a meta-analysis of 361,645 job applications spanning 1976 to 2020. The international team found a significant decline in discrimination against female applicants for traditionally male roles, with no observable bias in the last decade. Conversely, bias against male applicants for female-typed jobs has remained consistent. The belief that men are less communal than women has even intensified, highlighting the ongoing relevance of gender in workplaces. Rather than solely promoting female representation, decision-makers should challenge stereotypes and traditional roles for both genders, support men pursuing non-traditional roles, and work toward dismantling gender norms. Appcast’s gender bias decoder can assist with the recruiting pressures surrounding gender discrimination by identifying potential biases that exist in the wording of job ads.
Is it right (or even helpful) to spy on your employees?
As productivity growth has waned and remote work has become more prevalent, an increasing number of companies are contemplating the implementation of electronic performance monitoring (EPM). This involves observing, recording, and analyzing information about employee job performance. A meta-analysis of EPM found no evidence supporting the idea that it enhances worker performance. Instead, it is linked to increased worker stress, regardless of monitoring characteristics. The researchers caution against expecting guaranteed performance improvement from EPM investments, emphasizing that such systems can be a significant financial commitment. Organizations choosing to monitor electronically are recommended to use minimally invasive approaches. More invasive monitoring is associated with negative attitudes, counterproductive behaviors, and stress without performance benefits. Leaders are advised to make conservative monitoring decisions, focusing narrowly on task-relevant information, and limiting tracking of personal data unless necessary for safety. Transparency is crucial in EPM use, particularly with informing workers about monitoring details to minimize negative attitudes.
How does leadership impact mental health outcomes?
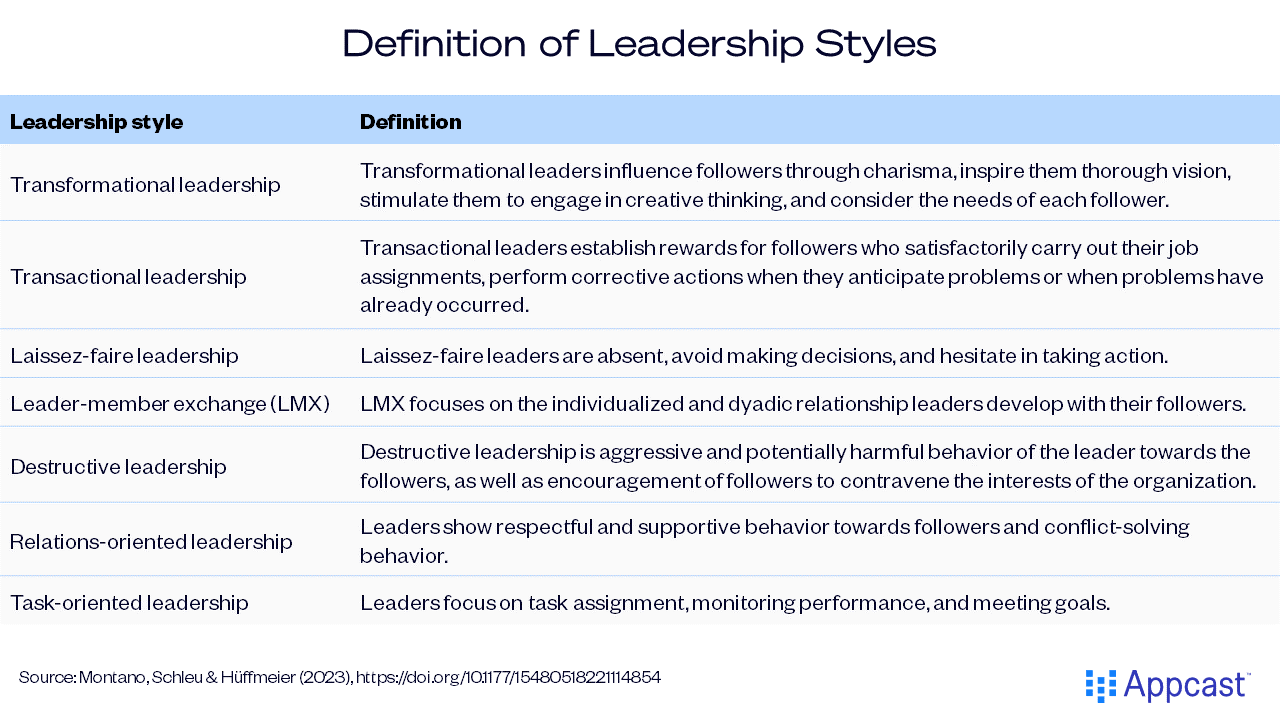
Companies are increasingly developing leadership strategies to boost employee experience and mental health. Yet, understanding of how various leadership styles influence mental well-being has been limited. A recent meta-analysis examined the impact of different leadership styles on mental health. The study reveals that transformational, relations-oriented, and task-oriented leadership positively impact mental health, while destructive and laissez-faire styles have a less favorable effect. To optimize leadership development, programs should prioritize cultivating behavioral traits linked to positive leadership patterns and address the detrimental impact of destructive leadership. Establishing ideal and negative leadership prototypes can guide expectations and foster positive qualities, discourage undesirable behaviors, and contribute to shaping organizational norms.
How does the organization of a team contribute to the creativity of a single worker?
Companies face increasing pressure to innovate, and team design provides valuable tools to boost creativity. Another meta-analysis explored how team design influences creativity and innovation in organizations. The study revealed a curvilinear relationship between team tenure and innovation: newly formed teams are less innovative, while the relationship is positive for long-established teams and weaker for moderately tenured teams. Additionally, the study highlights that autonomy-supportive leadership, task interdependence, and goal interdependence positively impact team creativity by enhancing team collaboration and potency. In terms of diversity, demographic diversity was unrelated to team creativity, but job-related diversity positively correlates with team creativity and innovation, likely due to cognitive processes such as diverse perspectives and information elaboration. Surprisingly, team size is unrelated to creativity and innovation, underscoring the importance of structuring tasks for interdependence and goals for common achievement.
As you can see, it’s been an eventful year in HR research. The insights described above (and more!) shift the way we view discrimination, employee well-being, and recruiting in general. While making time can be difficult, it’s important to keep your eye on the latest developments: Research and data play a powerful role in decision-making.


